oarsub¶
The user can submit a job with this command. So, what is a job in our context?
A job is defined by needed resources and a script/program to run. So, the user must specify how many resources and what kind of them are needed by his application. Thus, OAR system will give him or not what he wants and will control the execution. When a job is launched, OAR executes user program only on the first reservation node. So this program can access some environment variables to know its environment:
$OAR_NODEFILE contains the name of a file which lists all reserved nodes for this job $OAR_JOB_ID contains the OAR job identificator $OAR_RESOURCE_PROPERTIES_FILE contains the name of a file which lists all resources and their properties $OAR_JOB_NAME name of the job given by the "-n" option $OAR_PROJECT_NAME job project name
Options
-I, --interactive Request an interactive job. Open a login shell
on the first node of the reservation instead of
running a script.
-C, --connect=<job id> Connect to a running job
-l, --resource=<list> Set the requested resources for the job.
The different parameters are resource properties
registered in OAR database, and `walltime' which
specifies the duration before the job must be
automatically terminated if still running.
Walltime format is [hour:mn:sec|hour:mn|hour].
Ex: host=4/cpu=1,walltime=2:00:00
--array <number> Specify an array job with 'number' subjobs
--array-param-file <file> Specify an array job on which each subjob will
receive one line of the file as parameter
-S, --scanscript Batch mode only: asks oarsub to scan the given
script for OAR directives (#OAR -l ...)
-q, --queue=<queue> Set the queue to submit the job to
-p, --property="<list>" Add constraints to properties for the job.
(format is a WHERE clause from the SQL syntax)
-r, --reservation=<date> Request a job start time reservation,
instead of a submission. The date format is
"YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS".
--checkpoint=<delay> Enable the checkpointing for the job. A signal
is sent DELAY seconds before the walltime on
the first processus of the job
--signal=<#sig> Specify the signal to use when checkpointing
Use signal numbers, default is 12 (SIGUSR2)
-t, --type=<type> Specify a specific type (deploy, besteffort,
cosystem, checkpoint, timesharing)
-d, --directory=<dir> Specify the directory where to launch the
command (default is current directory)
--project=<txt> Specify a name of a project the job belongs to
-n, --name=<txt> Specify an arbitrary name for the job
-a, --anterior=<job id> Anterior job that must be terminated to start
this new one
--notify=<txt> Specify a notification method
(mail or command to execute). Ex:
--notify "mail:name@domain.com"
--notify "exec:/path/to/script args"
--resubmit=<job id> Resubmit the given job as a new one
-k, --use-job-key Activate the job-key mechanism.
-i, --import-job-key-from-file=<file>
Import the job-key to use from a files instead
of generating a new one.
--import-job-key-inline=<txt>
Import the job-key to use inline instead of
generating a new one.
-e --export-job-key-to-file=<file>
Export the job key to a file. Warning: the
file will be overwritten if it already exists.
(the %jobid% pattern is automatically replaced)
-O --stdout=<file> Specify the file that will store the standart
output stream of the job.
(the %jobid% pattern is automatically replaced)
-E --stderr=<file> Specify the file that will store the standart
error stream of the job.
(the %jobid% pattern is automatically replaced)
--hold Set the job state into Hold instead of Waiting,
so that it is not scheduled (you must run
"oarresume" to turn it into the Waiting state)
-s, --stagein=<dir|tgz> Set the stagein directory or archive
--stagein-md5sum=<md5sum> Set the stagein file md5sum
-D, --dumper Print result in DUMPER format
-X, --xml Print result in XML format
-Y, --yaml Print result in YAML format
-J, --json Print result in JSON format
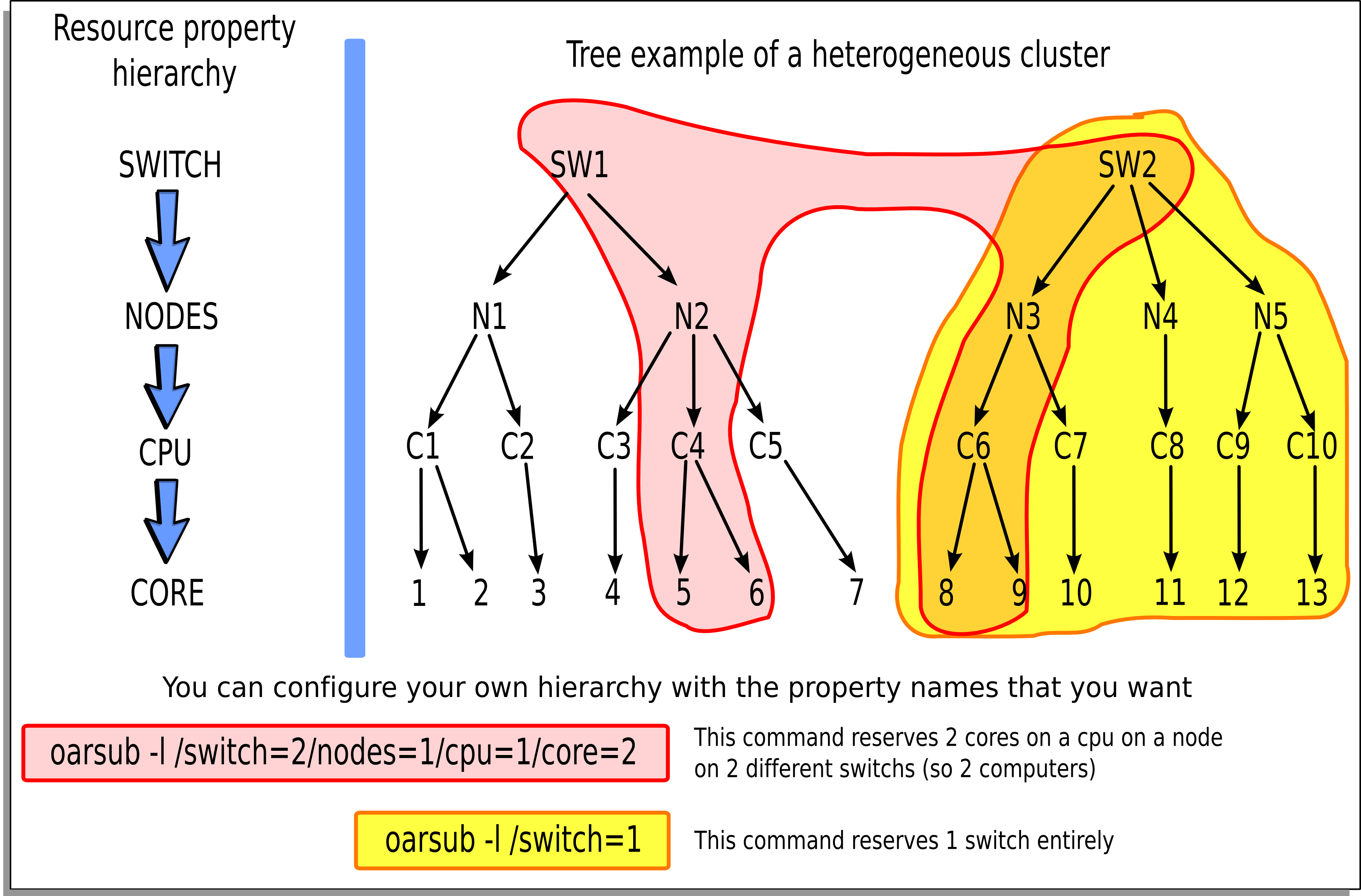
Wanted resources have to be described in a hierarchical manner using the “-l” syntax option.
Moreover it is possible to give a specification that must be matched on properties.
So the long and complete syntax is of the form:
"{ sql1 }/prop1=1/prop2=3+{sql2}/prop3=2/prop4=1/prop5=1+...,walltime=1:00:00"
- where:
- sql1 : SQL WHERE clause on the table of resources that filters resource names used in the hierarchical description
- prop1 : first type of resources
- prop2 : second type of resources
- + : add another resource hierarchy to the previous one
- sql2 : SQL WHERE clause to apply on the second hierarchy request
- ...
So we want to reserve 3 resources with the same value of the type prop2 and with the same property prop1 and these resources must fit sql1. To that possible resources we want to add 2 others which fit sql2 and the hierarchy /prop3=2/prop4=1/prop5=1.
Examples
# oarsub -l /nodes=4 test.sh
(the “test.sh” script will be run on 4 entire nodes in the default queue with the default walltime)
# oarsub --stdout='test12.%jobid%.stdout' --stderr='test12.%jobid%.stderr' -l
/nodes=4 test.sh
...
OAR_JOB_ID=702
...
(same example than above but here the standard output of “test.sh” will be written in the file “test12.702.stdout” and the standard error in “test12.702.stderr”)
# oarsub -q default -l /nodes=10/cpu=3,walltime=2:15:00 \
-p "switch = 'sw1'" /home/users/toto/prog
(the “/home/users/toto/prog” script will be run on 10 nodes with 3 cpus (so a total of 30 cpus) in the default queue with a walltime of 2:15:00. Moreover “-p” option restricts resources only on the switch ‘sw1’)
# oarsub -r "2009-04-27 11:00:00" -l /nodes=12/cpu=2
(a reservation will begin at “2009-04-27 11:00:00” on 12 nodes with 2 cpus on each one)
# oarsub -C 42
(connects to the job 42 on the first node and set all OAR environment variables)
# oarsub -p "not host like 'nodename.%'"
(To exclude a node from the request)
# oarsub -I
(gives a shell on a resource)